Hip Fracture vs Hip Replacement: When and Why Is Replacement Chosen?
A hip fracture is a serious injury, especially in older adults. Most occur after a fall or accident and can quickly limit a person’s ability to move or stand. The type and severity of the fracture determine the appropriate treatment. Some fractures can be reconstructed and stabilized using fixation, such as pins, plates, or screws. In other cases, a hip replacement (arthroplasty) may be the best option to restore mobility and reduce pain. Understanding the options helps patients and families make informed decisions about care.
Types of Hip Fractures
Hip fractures are classified by location in the femur. The most common types are femoral neck fractures and intertrochanteric fractures. A femoral neck fracture occurs just below the ball of the hip. The blood supply here is delicate, which can make healing difficult. If blood flow is lost, surgeons often recommend hip replacement instead of fixation. An intertrochanteric fracture occurs between the neck and shaft of the femur. This area has better blood circulation, so fixation is often successful.
When Fixation Works Best
Fixation works when the fracture is stable and bone quality is good. It is commonly used in younger patients to preserve the natural joint. Plates or screws realign and stabilize the bone, which then heals over time. Patients gradually return to activity as the bone strengthens.
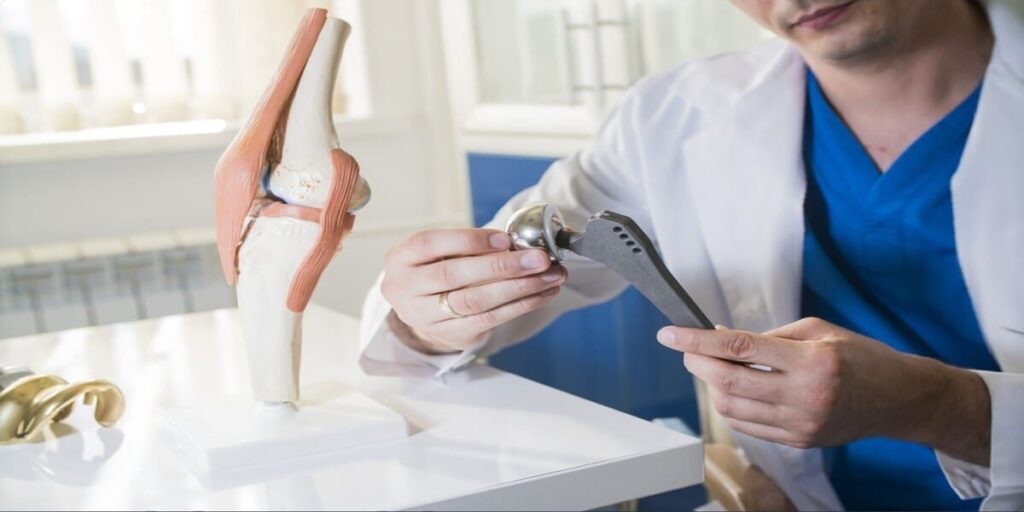

When Arthroplasty Is the Better Choice
Hip replacement is usually best for severe or displaced fractures. Damaged bone and cartilage are replaced with a prosthesis. This approach reduces pain, restores mobility faster, and lowers complications from poor bone healing. Older patients, especially with osteoporosis or poor blood supply, benefit from early rehabilitation and regained independence.
Balancing Risks and Benefits
Fixation preserves the patient’s bone and often requires shorter surgery, but healing may be slower, and stiffness or pain can occur. Hip replacement provides long-term relief and improved mobility, though rehabilitation is critical to prevent complications like infection or dislocation. Modern techniques make these risks minimal.
Conclusion
Choosing between fixation and hip replacement depends on age, bone quality, fracture type, and other health factors. Younger patients with stable fractures may benefit from fixation. Elderly patients or those with complex fractures often do better with arthroplasty. If you or a loved one is recovering from a hip injury, expert guidance is crucial. Dr. Arun Jyothi, a leading hip replacement surgeon, offers advanced treatments and rehabilitation plans to ensure recovery. Schedule a consultation to restore mobility and comfort.